
Further intraoperative interventions are based on the reducibility and postreduction stability of the DRUJ. DRUJ and elbow forGaleazzi fracturesMonteggia fracturescompartment. Anatomic reduction and rigid fixation should be followed by intraoperative assessment of the DRUJ. View Radius and Ulnar Shaft Fractures - Trauma - Orthobullets.pdf from AA 1 Yun. Open reduction and internal fixation is the preferred surgical option. In adults, nonsurgical treatment typically fails because of deforming forces acting on the distal radius and DRUJ.


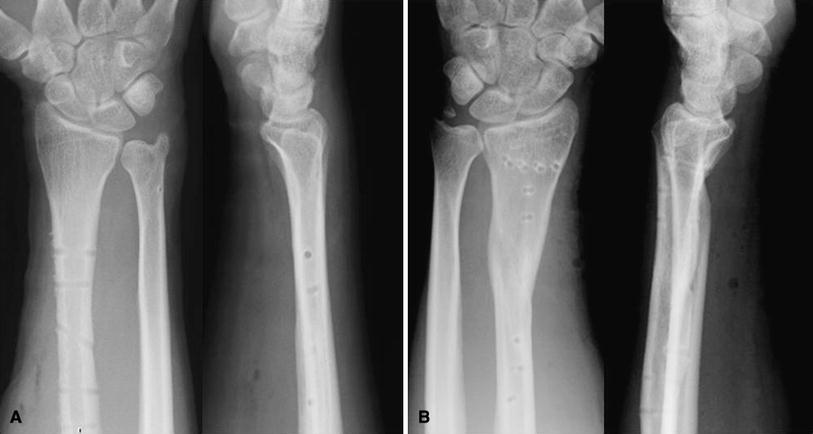
Nonsurgical management with anatomic reduction and immobilization in a long-arm cast has been successful in children. Underdiagnosis is common because disruption of the ligamentous restraints of the DRUJ may be overlooked. Diagnosis is established on radiographic evaluation. Whilst any fracture can become open, the most common fractures are tibial, phalangeal, forearm, ankle, and metacarpal. It classically involves an isolated fracture of the junction of the distal third and middle third of the radius with associated subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint the injury disrupts the forearm axis. In this episode, we review the high-yield topic of Galeazzi Fractures from the Trauma section. The Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the distal third of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. Typically, the mechanism of injury is forceful axial loading and torsion of the forearm. Listen to this episode from The Orthobullets Podcast on Spotify.
#Galeazzi fracture orthobullets code#
Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the radial diaphysis with disruption at the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). QBank Search Questions My TestMaster Create Personal Test Create Group Test Enter Test Code Active Test Cases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
